

Benzodiazepine Overdose Treatmentįlumazenil is an FDA-approved medication to reverse benzodiazepine overdose.
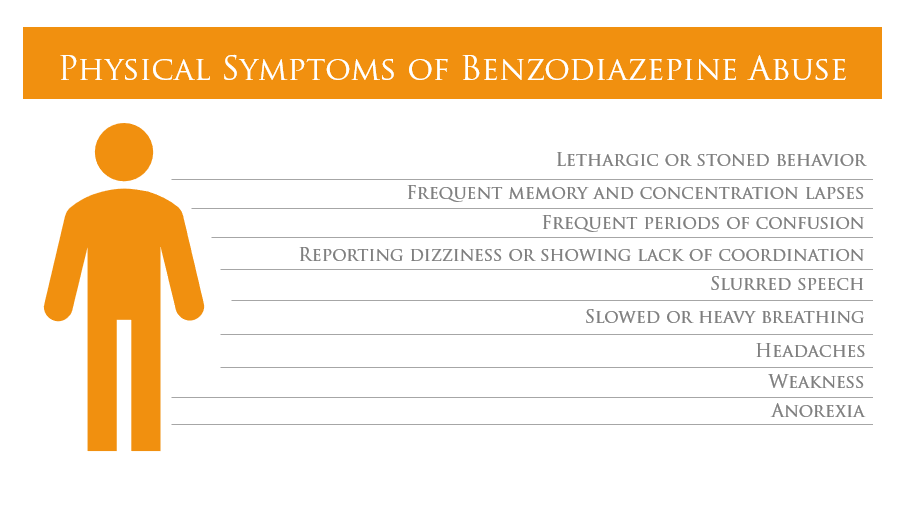
Old age and the use of other drugs are the major risk factors for complications from benzo overdose, which include death. Because of the risk of overdose, the CDC recommends against mixing benzos and opioids Use with other sedating drugs, such as opioids.Other risk factors specific to benzodiazepine overdose include:
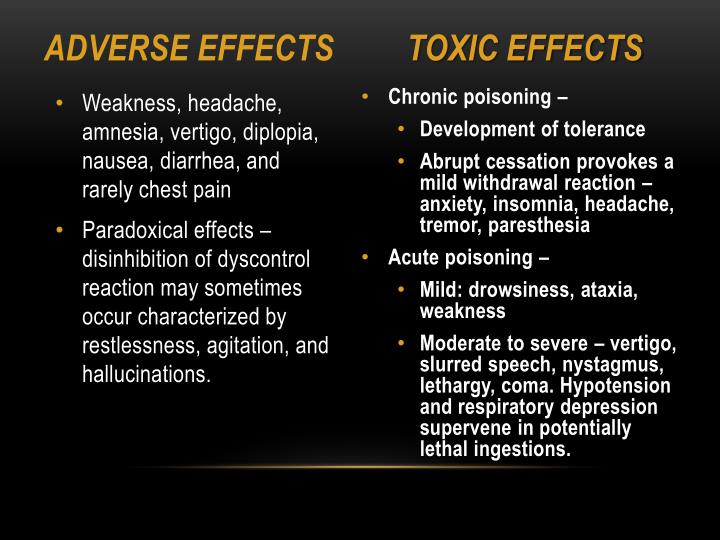

There are also increased risks related to benzo use in elderly people. Taking benzos and alcohol can cause overdose risks to increase. Having more than five doctors prescribing a controlled substance.crushing and snorting pills that are meant to be swallowed) Taking a drug through an unapproved route (ex.More than 90% of accidental drug overdose deaths have at least one of the following risk factors: Patients who are symptomatic will need 1:1 nursing in an HDU or equivalent environment until symptoms have resolved.Certain risk factors are common in overdoses, regardless of the drug.Caution is advised as it can precipitate a cholinergic crisis if given inappropriately. Physostigmine can be used both diagnostically (if patient returns to normal post administration) or an adjunct if anticholinergic delirium is not controlled with benzodiazepines.Once delirium has occurred it will be very difficult to administer and should be avoided.50g of activated charcoal maybe given to the alert and cooperative patient who has ingested benztropine in the previous 2 hours.EUC, CT brain and lumbar puncture maybe required in the undifferentiated patient.Screening: 12 lead ECG, BSL, Paracetamol level.Bladder scan and a catheter for urinary retention.diazepam 2.5 – 5 mg every 5 minutes IV until gentle sedation is achieved Titrated doses of benzodiazepines e.g.Controlling the delirium can be difficult, things to consider include.Sometimes therapeutic doses can cause an anticholinergic toxidrome.Effects are usually seen within 6 hours and may last anywhere between 12 hours to 5 days.Any overdose can cause an anticholinergic toxidrome that will likely require supportive care.Possible hepatic metabolism but excreted in the urine.It contains a combination of atropine (active part of atropine) and an antihistamine (diphenylmethyl) therefore it acts as an anticholinergic as well as a antihistaminergic with dopamine reuptake inhibition. You may also use it yourself as an antidote for an acute dystonic reaction. Benztropine is a potent anticholingeric in overdose. Normally used to ameliorate dyskinesia from antipsychotics but has been used for recreational purposes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
